- home > News > Filter knowledge
Is photocatalytic oxidation effective for air purification
The photocatalytic oxidation method refers to the use of some semiconductor materials with photoelectric effect as a catalyst, and the catalytic oxidation method is carried out under the action of light. This may be difficult to understand, but it is called "photocatalyst" in Japanese.
The photocatalytic oxidation method was discovered by Fujishima and Honda in Japan in the 1970s when they were studying the catalytic effect of TiO2. When the semiconductor TiO2 is irradiated with ultraviolet light with a wavelength of less than or equal to 387.5nm, the electrons in the step band will jump to the conduction band to generate holes. In the process of recombination, holes can easily capture the electrons on the organic matter on the surface of the particles to activate and oxidize these substances. The electrons that jump to the conduction band have strong reducibility and can reduce the substances adsorbed on the surface. In layman's terms, TiO2 can produce redox reactions on substances adsorbed on its surface under the irradiation of ultraviolet light, and decompose organic substances. When conditions permit, photocatalyst can play a very good role in sterilizing and removing TVOC.
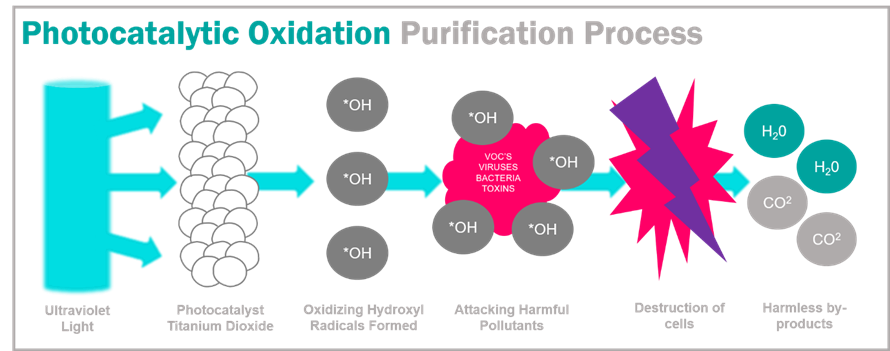
In addition to TiO2, semiconductors that can be used as photocatalysts include ZnO, CdS, SnO2, etc. Because TiO2 has high stability, good photoelectric effect, and harmless to the human body, it is the main component of photocatalyst. However, the conditions for its catalytic oxidation are relatively high. Later studies have found that some other substances can be infiltrated to modify the catalyst so that it can absorb a wider range of light, which is more practical. As a result, many formulas and technologies have been derived, and experts with Chinese characteristics have also created many terms such as nano-photocatalyst, cold catalyst, photohydrogen ion, CH-CUT, etc., which often make people fall into the cloud. In fact, no matter what the name is, the principle of conservation of energy must be observed. To produce redox reactions, there must be a sufficient supply of energy.
The catalytic efficiency of photocatalyst is affected by many conditions, such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, wind speed, etc., and it must be in contact with the surface of the photocatalyst to work (explained above), so in actual applications, it is more commonly used in The exterior walls and glass of the building are cleaned. Because there is sufficient sunlight (to catalyze oxidation) and rain washing (to regenerate the catalyst), the building is naturally kept clean. The effect is not obvious in air purification applications.
We often hear the propaganda about the removal of formaldehyde by photocatalyst, and usually there is only theoretical effect. There are even some unscrupulous merchants who know that photocatalyst is not effective in removing formaldehyde, but under the banner of photocatalyst, they use a blocking agent to treat formaldehyde and prevent the emission of formaldehyde. The treatment effect is very obvious in a short time, but after the blocking agent fails, Formaldehyde is still diffuse.
Next:下一篇:250 ℃ VS 400 ℃ High Temperature Resistant HEPA Filter

